Treatments Hormonal Imbalances Diabetes
A Comprehensive Guide to Diabetes and Its Management
Homeopathy views diabetes as a manifestation of an imbalance within the body, rather than simply focusing on the symptoms. It recognizes that each individual is unique and requires personalized treatment. Homeopathic remedies are selected based on the individual's specific symptoms, mental and emotional state, and physical constitution. Homeopathy is not meant to replace conventional medical treatment for diabetes. Instead, it can be used as a complementary approach to enhance overall well-being and support the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels. It is crucial to work in collaboration with a healthcare team that includes both a homeopath and a medical doctor to ensure comprehensive and safe management of diabetes.
Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body either does not produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin it produces. This leads to elevated blood sugar levels, which, if left uncontrolled, can cause serious complications. However, with proper management, individuals with diabetes can lead healthy and fulfilling lives. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of diabetes, including its types, causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies.
Types of Diabetes
There are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes.
Causes and Risk Factors:
The exact causes of diabetes are not yet fully understood, but several risk factors contribute to its development:
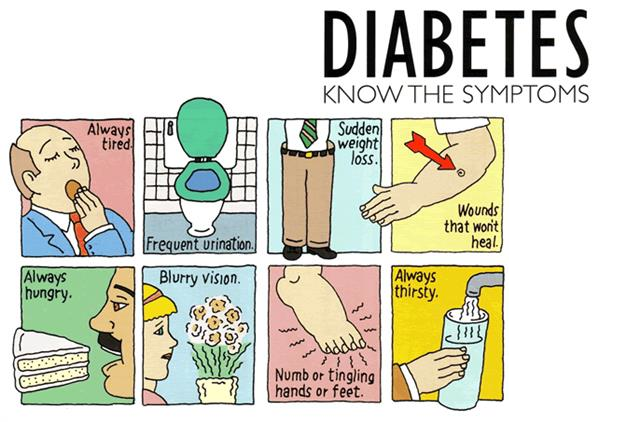
Sign & Symptoms :
Common symptoms of diabetes include:
Effective Diabetes Management Strategies
While diabetes is a lifelong condition, its impact can be minimized through effective management strategies:
Understanding Diabetes from a Homeopathic Perspective
Homeopathy views diabetes as a manifestation of an imbalance within the body, rather than simply focusing on the symptoms. It recognizes that each individual is unique and requires personalized treatment. Homeopathic remedies are selected based on the individual’s specific symptoms, mental and emotional state, and physical constitution.
Treating the Person, not the Disease
In homeopathy, the goal is to stimulate the body’s innate healing ability and restore its natural balance. The homeopath takes into consideration the person’s overall health, family history, lifestyle, and emotional well-being when selecting remedies. By treating the individual as a whole, homeopathy aims to address the root cause of the disease and not just its outward symptoms.
Complementary Approach to Conventional Treatment
Homeopathy is not meant to replace conventional medical treatment for diabetes. Instead, it can be used as a complementary approach to enhance overall well-being and support the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar levels. It is crucial to work in collaboration with a healthcare team that includes both a homeopath and a medical doctor to ensure comprehensive and safe management of diabetes.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to homeopathic remedies, lifestyle modifications play a vital role in managing diabetes effectively. A balanced diet, regular exercise, stress reduction, and proper sleep are essential for maintaining optimal health. Homeopathy can complement these lifestyle changes by addressing the underlying imbalances and supporting the body’s self-healing capacity.
Individualized Treatment and Monitoring
Dr. Singh’s Homeopathy recognizes the importance of individualized treatment and regular monitoring. The progress of each person’s case is carefully evaluated, and remedies may be adjusted accordingly. It is crucial to maintain open communication with the homeopath and medical doctor to ensure proper coordination and monitoring of blood sugar levels.
Conclusion:
Diabetes is a challenging condition that requires diligent management to prevent complications and maintain a good quality of life. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, adhering to prescribed medications, and staying proactive in diabetes management, individuals can successfully control their blood sugar levels and minimize the risk of long-term complications. Regular communication with healthcare professionals and a strong support system are essential in the journey of living well with diabetes. Remember, with proper management, diabetes doesn’t have to define or limit your life.

