Fatty Liver
A Comprehensive Guide to Fatty liver Disease
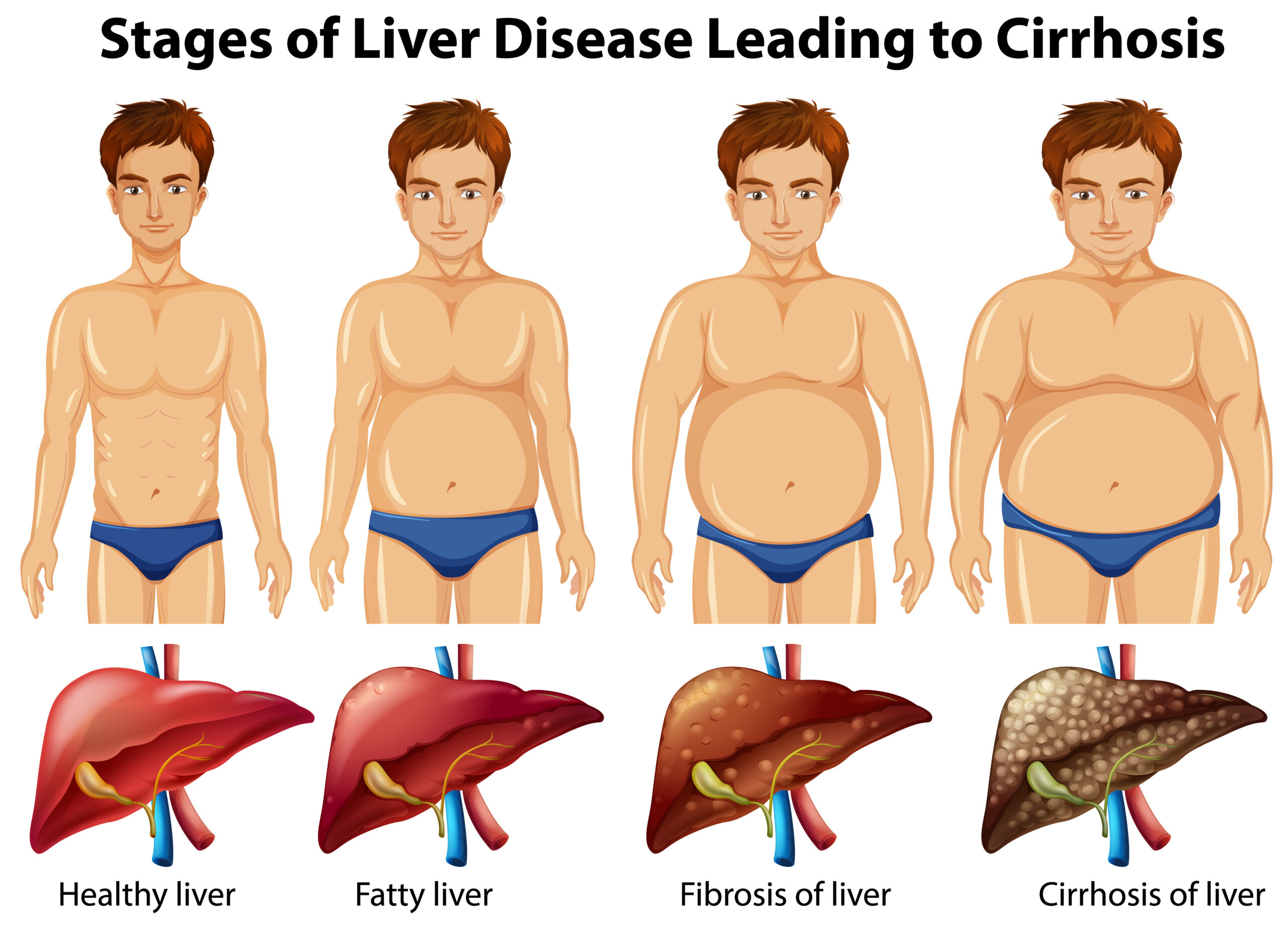
Fatty liver, or hepatic steatosis, is a condition where excess fat builds up in liver cells. It can be caused by factors such as obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, and metabolic disorders like diabetes. Often asymptomatic, it can progress to liver inflammation, fibrosis, or cirrhosis if left untreated. Management includes lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and avoiding sugar and alcohol.
Fatty liver disease, also known as hepatic steatosis, is an increasingly common condition characterized by the accumulation of excess fat in the liver. This buildup can lead to inflammation and liver damage, potentially progressing to more severe liver diseases. Here, we explore the types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, prevention, and homeopathic management of fatty liver disease.
Types of Fatty Liver Disease
– Simple Fatty Liver: Fat accumulates in the liver without inflammation or liver cell damage.
– Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): Fat buildup is accompanied by inflammation and liver cell damage, which can lead to fibrosis or cirrhosis.
– Caused by excessive alcohol consumption, leading to fat accumulation and liver damage.
Causes of Fatty Liver Disease
Symptoms of Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease often presents with no symptoms, especially in the early stages. However, as the condition progresses, symptoms may include:
– Fatigue
– Weakness
– Abdominal discomfort or pain (especially in the upper right side)
– Weight loss
– Loss of appetite
– Nausea
– Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes in severe cases)
Diagnosis of Fatty Liver Disease
Diagnosing fatty liver disease typically involves:
– Physical Examination: Checking for an enlarged liver.
– Blood Tests: Elevated liver enzymes (ALT and AST) can indicate liver inflammation.
– Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI can detect fat accumulation in the liver.
– Liver Biopsy: A small sample of liver tissue is examined to determine the extent of fat accumulation and liver damage.
Prevention of Fatty Liver Disease
Preventing fatty liver disease involves lifestyle changes and healthy habits:
Homeopathic Management of Fatty Liver Disease
Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to managing fatty liver disease by focusing on individual symptoms and overall well-being. Some commonly used homeopathic remedies include:
Conclusion
Fatty liver disease is a growing health concern that can have serious implications if left unmanaged. By understanding its types, causes, symptoms, and methods of diagnosis, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this condition. Dr. Singh’s Homeopathy provides a natural, personalized approach to support liver health and address the underlying factors contributing to fatty liver disease. Always consult a Qualified homeopathic practitioner to tailor the treatment to your specific needs and ensure a holistic approach to liver health.
Disclaimer:
This blog is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. The information provided is not a substitute for professional medical diagnosis or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay seeking it because of something you have read in this blog.

